Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kikuchi, Shin; Sakamoto, Kan*; Takai, Toshihide; Yamano, Hidemasa
Nihon Kikai Gakkai 2020-Nendo Nenji Taikai Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2020/09
In a postulated severe accidental condition of sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR), eutectic melting between boron carbide (B C) as control rod element and stainless steel (SS) as control rod cladding or related structure may occur. Thus, behavior of B
C) as control rod element and stainless steel (SS) as control rod cladding or related structure may occur. Thus, behavior of B C-SS eutectic melting is one of the phenomena to evaluate the core disruptive accidents in SFR. In order to clarify the kinetic feature of B
C-SS eutectic melting is one of the phenomena to evaluate the core disruptive accidents in SFR. In order to clarify the kinetic feature of B C-SS eutectic melting process in the interface, the thinning test for SS crucibles using the pellets of B
C-SS eutectic melting process in the interface, the thinning test for SS crucibles using the pellets of B C or SS with low B
C or SS with low B C concentration were performed to obtain the rate constant with dependence of B
C concentration were performed to obtain the rate constant with dependence of B C concentration against SS. It was found that the rate constants of eutectic melting between SS and SS low B
C concentration against SS. It was found that the rate constants of eutectic melting between SS and SS low B C concentration were smaller than that of B
C concentration were smaller than that of B C-SS in the high temperature range. Besides, the rate constant of eutectic melting between SS and B
C-SS in the high temperature range. Besides, the rate constant of eutectic melting between SS and B C containing SS became small when decreasing the B
C containing SS became small when decreasing the B C concentration against SS.
C concentration against SS.
Ebihara, Kenichi; Saito, Kei*; Takai, Kenichi*
Proceedings of 2016 International Hydrogen Conference (IHC 2016); Materials Performance in Hydrogen Environments, p.470 - 477, 2017/00
For understanding hydrogen (H) embrittlement of steels, it is necessary to infer the state that defects trap H in the steels. Thermal desorption spectra of H obtained by the thermal desorption spectrometry (TDS) are used for inferring such a state. Because the thermal desorption spectra include the influence of experimental conditions and hydrogen diffusion as well as information of the defects trapping H, it is necessary to interpret the spectra using the numerical simulation. In the presentation, we determined the detrapping and the trapping rate constants which are necessary for the simulation from the experimental spectra obtained for plate specimens which is so small that H diffusion is ignorable. Then we confirmed that the model using the obtained rate constants can simulate the spectra of larger cylindrical specimens, so that it was found that the rate constant for small specimens can be used for the simulation of the spectra for specimens of different shape or size.
Nagaishi, Ryuji; Inoue, Masao; Hino, Ryutaro; Ogawa, Toru
Proceedings of 2014 Nuclear Plant Chemistry Conference (NPC 2014) (USB Flash Drive), 9 Pages, 2014/10
Since seawater has been used as a coolant for reactors and spent fuel pools in broken reactor buildings at Fukushima Daiichi NPS accident, radioactive contaminated water emitted following the accident has contained salt content of seawater at high concentrations, different from that at TMI-2 accident. Radiolysis of seawater leading to hydrogen generation and corrosion has been simulated and reported by several groups. However, the proposed radiolysis models cannot be always applied to water radiolysis at the wide range of salt concentrations present in the NPS, mainly because primary yields of radiolysis products of water and radiation-induced reactions are dependent on the salt concentration. In this study, the radiolytic behavior in diluted and concentrated systems of seawater was considered on the basis of results in steady state and pulse radiolysis experiments, in which the above salt effects were demonstrated from the obtained results.
JNC TN8400 2000-012, 33 Pages, 2000/04
The redox condition of near-field is expected to affect the performance of engineered barrier system. Especially, the oxygen initially existing in the pore space of compacted bentonites strongly affects the redox condition of the near-field. For assessing the influence of the oxygen, the transport parameters of it in the compacted bentonite and consumption process should be known. Therefore, following researches were conducted. In order to understand the diffusion of dissolved oxygen (DO) in compacted bentonite and to predict the effect of DO, the effective diffusion coefficients of DO in compacted sodium bentonite were measured by electrochemistry. As the results, the following relationship between the dry density of compacted sodium bentonite and the effective diffusion coefficient of DO in compacted sodium bentonite was derived: De=1.53 0.13
0.13 10
10 exp(-2.15
exp(-2.15 0.24
0.24 10
10 p) where De is the effective diffusion coefficient (m
p) where De is the effective diffusion coefficient (m s
s ) of DO in compacted sodium bentonite and
) of DO in compacted sodium bentonite and  is the dry density (kg m
is the dry density (kg m ) of compacted sodium bentonite. The oxygen concentration in the bentonite is expected to be controlled by oxidation of pyrite as impurity in the bentonite. In order to investigate the above idea, the rates of pyrite oxidation by DO in compacted sodium bentonite were estimated from the experimental data on pyrite-bentonite systems usig the obtained effective diffusion coefficient of DO. The results show that the averages of the rate constants of pyrite oxidation by DO in the bentonite for dry densities of 0.8, 0.9, 1.0, 1.1 and 1.2
) of compacted sodium bentonite. The oxygen concentration in the bentonite is expected to be controlled by oxidation of pyrite as impurity in the bentonite. In order to investigate the above idea, the rates of pyrite oxidation by DO in compacted sodium bentonite were estimated from the experimental data on pyrite-bentonite systems usig the obtained effective diffusion coefficient of DO. The results show that the averages of the rate constants of pyrite oxidation by DO in the bentonite for dry densities of 0.8, 0.9, 1.0, 1.1 and 1.2 10
10 kgm
kgm were 1.38
were 1.38 0.32
0.32 10
10 , 1.10
, 1.10 0.24
0.24 10
10 , 1.16
, 1.16 0.35
0.35 10
10 , 9.36
, 9.36 2.23
2.23 10
10 and 7.48
and 7.48 1.92
1.92 10
10 ms
ms , respectively. The relationship between the dry density (
, respectively. The relationship between the dry density ( ) and the rate constant (k') was expressed as follows: k'=3.94
) and the rate constant (k') was expressed as follows: k'=3.94 1.06
1.06 10
10 exp(-1.33
exp(-1.33 0.28
0.28 10
10
 ) ...
) ...
Miki, Takahito*; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Chiba, Tamotsu*; Inagaki, Manabu*; Yui, Mikazu
JNC TN8400 2000-007, 32 Pages, 2000/01
This report presents a summary of literature survey about geochemical reactions which are important to evaluate the redox conditions in the near field rock mass and buffer. The results of literature survey are summarized as follows; (1)Minerals including ferrous iron and organic materials in the rock mass are important reductants. Initial stage after closure of repository, oxygen will be consumed by pyrite, because the reaction rate between pyrite and oxygen is relatively fast. (2)It is possible to estimate the redox capacity for reductants by rock (mineral)-water iteraction experiment in a laboratory. And it is expected that the ferrous iron-rich rock and higher porosity rock may have bigger redox capacity. (3)It is possible to estimate the oxygen consumption rate by reductants such as minerals including ferrous iron. The rate law and rate constant for the oxidation reaction of ferrous iron in the solution are also determined. As a conclusion, it seems that we can evaluate kinetically the evolution of geochemical conditions in the near field rock mass and buffer by excavation of drifts, based on data derived from these existing literatures.
Arthur, R. C,*; Savage, D.*; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Shibata, Masahiro; Yui, Mikazu
JNC TN8400 2000-005, 61 Pages, 2000/01
Kinetic data, including rate constants, reaction orders and activation energies, are compiled for 34 hydrolysis reactions involving feldspars, sheet silicates, zeolites, oxides, pyroxenes and amphiboles, and for similar reactions involving calcite and pyrite. The data are compatible with a rate law consistent with surface reaction control and transition-state theoly, which is incorporated in the geochemieal software package EQ3/6 and GWB. Kinetic data for the reactions noted above are strictly compatible with the transition-state rate law only under far-from-equilibrium conditions. It is possiblethat the data are conceptually consistent with this rate law under both far-from-equilibrium and near-to-equilibrium conditions, but this should be confirmed whenever possible through analysis of original experimental results, Due to limitations in the availability of kinetic data for mineral-water reactions, and in order to simplify evaluations of geochemical models of groundwater evolution, it is convenient to assume local-equilibrium in such models whenever possible. To assess whether this assumption is reasonable, a modeling approach accounting for coupled fluid flow and water-rock interaction is described that can be used to estimate spatial and temporal scale of local equiliblium. The approach is demonstrated for conditions involving groundwater flow in fractures at JNC's Kamaishi in-situ tests site, and is also used to estimate the travel time necessary for oxidizing surface waters to migrate to the level of a HLW repository in crystalline rock. The question of whether local equilibrium is a reasonable assumption must be addressed using an appropriate modeling approach. To be appropriate for conditions at the Kamaishi site using the modeling approach noted above, the fracture fill must closely approximate a porous medium, groundwater flow must be purely advective and diffusion of solutes across the fracture-host rock boundary must not occur. Moreover, the ...
 S and D
S and D S
SSato, K.*; *; *; *; *; Kurosaki, Yuzuru*; Takayanagi, Toshiyuki
Chemical Physics, 242(1), p.1 - 10, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:22.56(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
 D,
D, P)+CH
P)+CH and CD
and CD reactions; The Role of nonadiabatic transitions on thermal rate constants
reactions; The Role of nonadiabatic transitions on thermal rate constantsTakayanagi, Toshiyuki; Kurosaki, Yuzuru*; Sato, K.*; *; *; *
Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 103(2), p.250 - 255, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:71.42(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
 D,
D, P) with C
P) with C H
H and C
and C D
D between 225 and 292K
between 225 and 292KSato, K.*; *; *; *; *; Kurosaki, Yuzuru*; Takayanagi, Toshiyuki
Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 103(43), p.8650 - 8656, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:64.06(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
 ZrO
ZrO packed bed
packed bedKawamura, Yoshinori; Enoeda, Mikio; Okuno, Kenji
Fusion Engineering and Design, 39-40, p.713 - 721, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:57.28(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 elimination from 2,3-dimethylbutane cation: (CH
elimination from 2,3-dimethylbutane cation: (CH )
) CHCH(CH
CHCH(CH )
)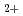
 (CH
(CH )
) C=C(CH
C=C(CH )
)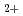 +H
+H ; An ab initio molecular orbital study
; An ab initio molecular orbital studyKurosaki, Yuzuru*; Takayanagi, Toshiyuki; Miyazaki, Tetsuro*
Journal of Molecular Structure; THEOCHEM, 452, p.209 - 218, 1998/00
no abstracts in English
 D,
D, P)+C
P)+C H
H and C
and C D
D reactions
reactionsTakayanagi, Toshiyuki; Kurosaki, Yuzuru*; *; *; *; Sato, K.*; *
Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 102(31), p.6251 - 6258, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:42 Percentile:78.25(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
 reaction
reactionTakayanagi, Toshiyuki; Kurosaki, Yuzuru*
Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 101(38), p.7098 - 7104, 1997/00
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:73.31(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
*; *; Koike, Tadao; Miyata, Teijiro
JAERI-Tech 96-056, 59 Pages, 1996/12
no abstracts in English
Ogawa, Hiromichi; Takebe, Shinichi;
JAERI-Research 94-002, 12 Pages, 1994/07
no abstracts in English
*; Tachimori, Shoichi; Naito, Shinjiro*
JAERI-M 93-056, 27 Pages, 1993/03
no abstracts in English
Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Kudo, Hiroshi; *; *
Radiochimica Acta, 63, p.167 - 171, 1993/00
no abstracts in English
Yoshida, Hiroshi; *; *; Enoeda, Mikio
JAERI-M 92-083, 28 Pages, 1992/06
no abstracts in English
*; Hirata, Masaru; Yahata, Taneaki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 28(8), p.739 - 747, 1991/08
no abstracts in English
; Tsuji, Toshihide*; *
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 28(8), p.721 - 731, 1991/08
no abstracts in English